BC547 Transistor – Versatile NPN/PNP Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
₹20
- BC557 Transistor can be used as Amplifier
- BC557 Transistor can be used as a switch
- Responsive to current
- Output impedance is less
- Life span is good
- Noise operation is less
- Circuit design is simple
- Uses less power supply
- Quick action at the circuit
Description
BC547 Transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor’s terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.
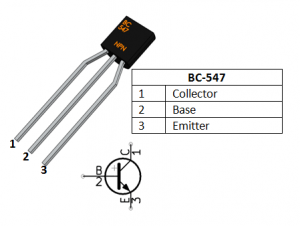
Features:-
• Advanced process technology
• Low error voltage
• Fast switching speed
• Full-voltage operation
• High power and current handling capability
Detailed Specifications:-
| Transistor Polarity | NPN |
| Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO) | 50VDC |
| Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) | 45VDC |
| Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO) | 6VDC |
| Continuous Collector Current (IC) | 100mA |
| Output Capacitance (Cobo) | 4.5pF |
| Transition Frequency (fT) | 300MHz |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 110-800 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55 – 150°C |
| Power Dissipation (PD) | 625mW |
BC547 transistor has a gain value of 110 to 800, this value determines the amplification capacity of the transistor. The maximum amount of current that could flow through the Collector pin is 100mA, hence we cannot connect loads that consume more than 100mA using this transistor. To bias a transistor we have to supply current to base pin, this current (IB) should be limited to 5mA.
When this transistor is fully biased then it can allow a maximum of 100mA to flow across the collector and emitter. This stage is called Saturation Region and the typical voltage allowed across the Collector-Emitter (VCE) or Base-Emitter (VBE) could be 200 and 900 mV respectively. When base current is removed the transistor becomes fully off, this stage is called as the Cut-off Region and the Base Emitter voltage could be around 660 mV.
BC547 as Switch
When a transistor is used as a switch it is operated in the Saturation and Cut-Off Region as explained above. As discussed a transistor will act as an Open switch during Forward Bias and as a Closed switch during Reverse Bias, this biasing can be achieved by supplying the required amount of current to the base pin. As mentioned the biasing current should maximum of 5mA. Anything more than 5mA will kill the Transistor; hence a resistor is always added in series with base pin. The value of this resistor (RB) can be calculated using below formulae.
RB = VBE / IB
Where, the value of VBE should be 5V for BC547 and the Base current (IB depends on the Collector current (IC). The value of IB should not exceed mA.
BC547 as Amplifier
A Transistors acts as an Amplifier when operating in Active Region. It can amplify power, voltage and current at different configurations.
Some of the configurations used in amplifier circuits are
- Common emitter amplifier
- Common collector amplifier
- Common base amplifier
Of the above types common emitter type is the popular and mostly used configuration. When uses as an Amplifier the DC current gain of the Transistor can be calculated by using the below formulae
DC Current Gain = Collector Current (IC) / Base Current (IB)
Applications
- Driver Modules like Relay Driver, LED driver etc..
- Amplifier modules like Audio amplifiers, signal Amplifier etc..
- Darlington pair
2D model of the component
If you are designing a PCD or Perf board with this component then the following picture from the Datasheet will be useful to know its package type and dimensions.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.01 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 5 × 8 × 2 cm |